Coolsculpting Waist Before And After
Completely get rid of fat deposits can, by spending a lot of time, effort and nerves.
This problem is equally relevant for both women and men, and the dream of a beautiful body without surgery and complications would remain a dream, if not for the methods of hardware cosmetology.
One of such safe and sufficiently effective procedures is coolsculpting or fat removal by means of low temperatures.
What is the basis of CoolSculpting?
Coolsculpting is the newest method of dosed and selective cold exposure, with the help of which a correction of the figure is achieved and excess fat is removed. With the help of this method, it is possible to work on individual problem areas and places of fat accumulation – buttocks, abdomen, forearms and hips.
The history of the discovery of this technique belongs to American scientists and physicians, and the method itself is considered non-invasive and effective, which allows it to be successfully applied in hardware cosmetology.
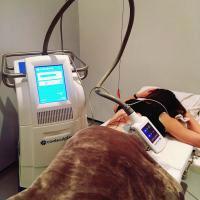
Excess Fat All The Way Around The Waistline
- The procedure of coolsculpting waist area consists in the ability of the melt to melt already at a temperature of 17-20 ° C.
- With the help of special applicators, body parts are gradually cooled to -5 C, causing fat deposits to crystallize.
- Lipid inclusions in the crystallization process become solid, and the cell membranes are damaged and die.
The mechanism of the effect of cryolipolysis used the ability of damaged cells to self-destruct, the process of which is called apoptosis.
This is a natural defense of the body from the “trash” and decay products that are formed in the tissues. Non-working and damaged cells, undergoing apoptosis, are removed by the lymphatic system, which performs purificatory function in our body.
The advantages of the method are obvious, because, in addition to safety, it is comfortable, does not need anesthesia and does not affect other tissues and cells of the body. The patient feels a slight cold during the procedure, which can quickly become used after 10 minutes.
After the session, the traces on the skin disappear in a short period of time (approximately after 2 -3 hours). The coolsculpting session on waist lasts 40-60 minutes, and the number of procedures is determined at the first examination by a doctor.
For small fat deposits, 1 or 2 sessions are required, and for large volumes – no more than 4 procedures, which are carried out at intervals not more than 1 time per month.
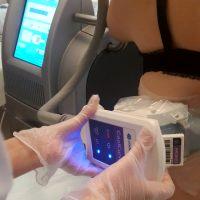
Excess Fat Around Your Waist
Such a break is necessary for the body for a natural mechanism of excretion of dead cells and decay products. It is proved that in one session you lose 6-8 cm in volume, and the amount of adipose tissue is reduced by 25-30%.
The technique differs from other procedures of the body correction in that the result becomes more noticeable over time, as the process of cell death lasts 60-80 days or more.
The first results can appear in 2 weeks, and the maximum effect will be visible only after 2 months.
Before the sessions of coolsculpting on waist, the doctor-cosmetologist on an individual consultation evaluates the type of physique and its features, measures the body mass index and weight, determines the percentage of excess fat and the number of necessary procedures.
It should be taken into account that in patients with obesity of 2-3 degrees this method for weight loss is contraindicated, since a large load is created on the internal organs, including the liver and lymphatic system.
Indications and contraindications to coolsculpting treatment
The procedure is indicated in cases when there is a presence of fatty folds and deposits in the area of the shoulders and forearms, abdomen, hips, waist.
However, this method also has contraindications, which you need to know about. Contraindications to cryolipolysis are determined by a doctor-cosmetologist and are as follows:
- Individual sensitivity of the skin to cold.
- Inflammatory diseases of the skin in the treated area.
- Obesity.
- The period of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Open wounds and violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of exposure.
- Mental disorders and epilepsy.
- Presence of cardiac stimulants and metal implants.
- Infectious diseases and the presence of a chronic foci of infection.
- Herniation of the abdomen (umbilical).
- Violation of the process of blood clotting.
- Kidney disease (kidney failure).
- Diseases of the liver and gallbladder.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Taking certain medications (hormone therapy).